White Box Penetration Testing: Definition, Pros & Cons, and Essential Guide
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, safeguarding software integrity is a top priority. White box penetration testing is a crucial cornerstone in the proactive defense strategy against emerging cyber threats. This detailed testing approach offers a unique viewpoint, much like a hacker’s perspective from inside the system, enabling a thorough exploration of potential vulnerabilities deeply embedded within the software.
As the digital world continues to expand and evolve, so do the sophisticated techniques of cyber attackers, white box penetration testing serves as a crucial tool in staying ahead of these threats by revealing weaknesses in the system’s core, allowing for proactive reinforcement of security measures.
Understanding the pivotal role of this method within software quality assurance is essential, as it not only identifies existing vulnerabilities but empowers organizations to proactively strengthen their software, fostering resilience against potential breaches and cyber-attacks.
What Is White Box Penetration Testing?
White box penetration testing definition, referred to as clear box or structural testing, is a technique that grants the tester access to the internal structure of the system to replicate a hacker’s actions and uncover potential vulnerabilities. This method provides a comprehensive understanding of the application, identifying all possible entry points into the system.
White box pentest is frequently employed to examine a system’s essential parts, particularly by companies that develop their software products, or integrate multiple applications. It is a method to evaluate a system’s security by assessing its capability to withstand various real-time attacks.

What is white box penetration testing?
Benefits of White Box Penetration Testing
An efficient white box penetration test helps avoid the issues, errors, and oversights that can leave your businesses vulnerable to hackers. Let’s explore more benefits of white-box penetration testing:
- Comprehensive oversights of possible issues: White box penetration testing offers the most comprehensive analysis of internal and external vulnerabilities from the internal point of view, which is not available to typical attackers.
- Early detection: White box penetration testing is integrated into the early development stages, when there is no user interface, and even before the software application is available to users, which enables detecting the vulnerabilities at a very early stage.
- Extensive testing coverage: White box penetration testing can identify weaknesses in areas that are unreachable for black box testing, for instance, an app’s source code, design, and business logic.
- Precise identification of weaknesses: Since testers have detailed knowledge of the internal workings of the system, they can pinpoint specific weaknesses, potential security gaps, and flaws in the code logic. This level of detail often leads to more accurate identification of vulnerabilities.

Benefits of white box penetration testing
Disadvantages of White Box Testing
Despite all the appealing advantages, white box penetration testing shows some drawbacks in certain situations:
- High programming language requirements: Implementing white-box penetration testing involves internal network testing, which requires the testers to be familiar with critical programming tasks, like performing port scanning, SQL injection, and common attacks. By this, they will have a better understanding of the potential access points.
- Limited real-world simulation: White box testing operates with complete knowledge of the system, which doesn’t accurately replicate real-world attack scenarios where attackers have limited or no knowledge. This approach might overlook vulnerabilities that would be apparent to external attackers working with less information.
- Risk of biased testing: Testers, armed with complete system details, might inadvertently focus on known weaknesses or areas they are more familiar with, potentially overlooking other vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers with different perspectives.

Disadvantages of white box penetration testing
Black Box, Grey Box and White Box Penetration Testing Differences
Black box, grey box and white box testing are all types of penetration testing – the practice of testing a computer system, network, or web app to find issues, errors, and vulnerabilities that an attacker could exploit.
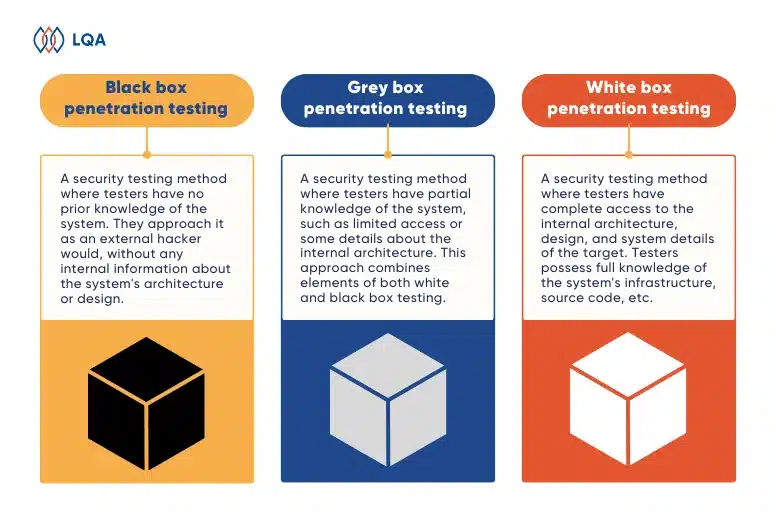
Black box, Grey box and White box penetration testing differences
To help you distinguish between black box, grey box and white box penetration testing, understand the benefits and limitations of each type, and when to apply it to get the best results, we have summarized it in the following comparison table:
| Aspects | Black box penetration testing | Grey box penetration testing | White box penetration testing |
| Level of knowledge requirement | Require little or no knowledge of infrastructure and network | Require basic knowledge of the internal codebase, architecture, and infrastructure | Allow complete access to knowledge about the system’s infrastructure, codebase, and network |
| Level of programming language requirement | Require no syntactic knowledge of the programming language | Require a basic comprehension of the programming language | Require high and professional understanding of programming language |
| Standard techniques | Boundary value analysis, Graph-Based testing, Equivalence partitioning, etc | Regression testing, Pattern testing, Matrix testing, Orthogonal array testing, etc | Decision coverage, Path testing, Branch testing, Statement coverage, etc |
| Advantages | – Mimics real-world attacks
– Provides an outsider’s perspective – Encourages creative problem-solving |
– Balances realism and deeper insights
– Enables access to some internal system knowledge – Optimize time and resources |
– Understands thoroughly of the system’s internals
– Delivers comprehensive coverage of system security |
| Disadvantages | – Limited insight into internal structures
– Incomplete view of vulnerabilities – Possible overlook of certain critical vulnerabilities |
– Restricted insight compared to White Box
– Dependent on available information – Possible miss of certain system areas |
– Time-consuming due to in-depth analysis – Costly due to skilled personnel and time- Prone to false positives if not done carefully |
| When to use | – Simulating external threats
– Testing overall security posture – Assessing response to unknown attackers |
– Balancing depth and efficiency
– Targeted testing with some internal insights – Limited access but need for deeper insight |
– Assessing specific system components
– Analyzing code, architecture, and design – Identifying and fixing intricate flaws |
The selection of Black Box, Grey Box, or White Box Penetration Testing depends on the level of internal knowledge required, the depth of the assessment needed, and the specific objectives of your security testing rpojects. It’s often beneficial to employ a combination of these methodologies for a comprehensive security assessment based on the unique needs of the system or software being evaluated.
White Box Penetration Testing Techniques
When it comes to software security testing, security testing white box techniques review source code (the internal structure of the software application) to detect gaps that can make an application vulnerable to cybersecurity threats.
One of the main goals of white box penetration testing is to cover the complete source code as extensively as possible. Three main types of techniques for use in white box penetration testing include Path coverage, Statement coverage, and Branch coverage.
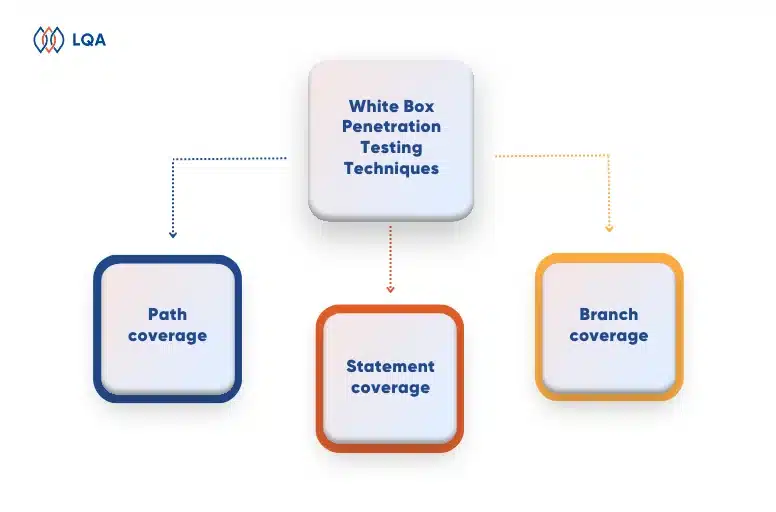
White Box Penetration Testing Techniques
Path coverage
This white box test methodology pays attention to all the paths. The path is a flow of execution that follows a set of instructions. The path coverage examines all possible paths of the software and ensures each path is traversed at least once. The path coverage is far more powerful than the branch coverage and is useful for testing complicated builds.
Statement coverage
Statement methodology checks if each functionality was tested one time. A statement indicates a functionality or set of actions for the application to decode depending on its programming language.
An executable statement is when the statement is put together and transformed into an object code, which will subsequently execute the action it was designed for. It helps to uncover unused or missing statements and branches as well as leftover dead codes.
The statement coverage evaluates if each line of code is executed at least once and helps find unnecessary or missing lines.
Branch coverage
A branch is one of many execution paths that the code can take after processing a decision statement like an if statement. This method is to confirm that all branch codes are tested.
The branch coverage is tested to check whether all branches in a codebase are exercised by tests and no branch leads to abnormal behavior of the application. It maps the code into branches of conditional logic and ensures that all branches are covered by unit tests.
One should ascertain that all codes have been launched at least once.
Common White Box Penetration Testing Tools
Several common tools/libraries employed in white-box penetration testing include:
- Metasploit: Penetration testers utilize Metasploit to create and authenticate exploit code before deploying it in real-world scenarios. It’s instrumental for network security testing or remote system intrusion.
- Nmap: As an open-source network administration tool, Nmap monitors network connections and scans extensive networks, aiding in host and service auditing as well as intrusion detection. It offers packet-level and scan-level analysis and is freely available for download.
- PyTest: Pytest, a comprehensive Python testing tool, facilitates writing more efficient programs, supporting test-driven development (TDD) and behavior-driven development (BDD).
- NUnit: NUnit is an open-source unit testing framework beneficial for the .NET Framework and Mono, aiding in writing better code and reducing application bugs.
- John the Ripper: This fast password cracker identifies weak Unix passwords and is compatible with various operating systems such as Unix, Windows, DOS, BeOS, and OpenVMS. John the Ripper supports multiple password hash types commonly found in Unix systems and other patches contributed by users.
- Wireshark: Functioning as a network traffic analyzer, Wireshark enables monitoring and analyzing traffic within system networks. It is open-source and widely recognized as the foremost network analyzer globally, primarily used by network administrators and professionals to troubleshoot network and system performance issues and filter various network protocols.
The tools employed in white-box penetration testing are similar to those used in other penetration tests, but the methodology for employing these tools differs significantly.
Essential White Box Penetration Testing Steps
A process of software white box penetration testing comprises the following steps:

Essential White box penetration testing steps
Source code review
The initial step is understanding the internal structure and functionality of a target software application. This crucial step requires a test engineer to review thoroughly the software’s source code, and understand clearly how it works in order to set the foundation for designing test cases that will help encounter security weaknesses.
Select the testing areas
After understanding completely the software’s internal structure and how it functions, the next step is determining the areas that need to be tested.
As the test aims to encompass every potential scenario for running code systematically, it proves more effective to explore the numerous possibilities within a smaller area rather than a larger one, as the latter wouldn’t ensure the same comprehensive coverage.
Covering a vast area is feasible, yet it demands significant effort, resources, and labor for test coverage. Consequently, it’s not recommended to execute this extensive coverage only on demand. For instance, it becomes essential in situations where it’s crucial to safeguard every aspect of the system; in such cases, it would be deemed necessary.
Code & flowchart identification
This step adds a structured approach to the white box penetration testing by visually mapping the code execution process, facilitating a more organized and systematic analysis of the system’s functionalities.
- Identify potential code lines: Thoroughly examine the system and identify all possible code segments associated with the functionalities or aspects under test. This involves a comprehensive review of the codebase, focusing on critical areas that could be potential sources of vulnerabilities.
- Create a flow chart: Outline the flow of the identified code segments. Create a flow chart or diagram to represent the flow of code execution, including input points, processing stages, and output results.
- Output tracing: Document and trace the output of each code segment within the flow chart. This helps in understanding how inputs are processed and how outputs are generated, aiding in the identification of potential vulnerabilities and understanding the system’s behavior.
Design test cases
Designing test cases is a pivotal phase in white box penetration testing, involving the creation of detailed scenarios for every identified code segment and system functionality.
Each test case outlines potential vulnerabilities, failure points, and specific testing procedures. It includes boundary testing, attack scenario simulations, and meticulous recording of testing outcomes to comprehensively evaluate the system’s security posture and ensure a systematic approach to identifying and addressing vulnerabilities.
Execute testing
The execution phase in white box security testing involves putting the devised plans into action, rigorously conducting tests according to the outlined strategies, and repeatedly iterating through the testing process until all identified systems are thoroughly examined, leaving no vulnerabilities unchecked.
This phase includes comprehensive testing, meticulous documentation of findings, validation of vulnerabilities, and continual refinement of testing procedures to ensure the system’s robust security against potential threats.
Reporting
Compile a detailed report that includes identified vulnerabilities, their potential impact, and recommendations for mitigation. This report should prioritize vulnerabilities based on their severity and guide how to address them.
Continuous improvement
Security is an ongoing process. Continuous monitoring, regular security assessments, and improvement in policies and practices are essential to maintain a robust security posture.
White Box Penetration Testing by LQA
Enhancing cybersecurity testing involves engaging a specialized security firm to assess your business’s vulnerabilities and deliver a detailed report with recommended solutions, a crucial step in preventing cyber attacks.
Having more than 7 years of experience, and as the pioneering independent software QA in Vietnam, LQA stands out as a prominent IT quality and security assurance firm, offering a complete range of penetration testing services to fortify businesses against security threats.

LQA software quality assurance awards
Alongside white box penetration testing services, LQA provides comprehensive software testing services including white box, black box, web application, mobile application, API, manual, and automation testing services.
At LQA, we maintain up-to-date expertise on the latest threats, attacks, and vulnerabilities, employing industry-leading tools to conduct comprehensive penetration tests.

LQA robust software testing tools
Key features of LQA’s white box cyber security solution:
- Comprehensive software QA solutions covering consulting, planning, execution, and ongoing support.
- Ensured bug rate lower than 3% for devices, mobile, and web applications.
- Rapid delivery facilitated by a diverse pool of proficient testers.
- Optimal price-to-quality ratio, leveraging cost benefits and expertise of Vietnamese IT human resources.
- Tailored solutions based on industry-specific experience.
- Maximum security ensured through a Non-disclosure Agreement (NDA) and best security practices during database access.
Connect with LQA’s experts to safeguard your data and assets from potential hackers today!
Frequently Asked Questions about Haptic Feedback
1. What is white box penetration testing?
White box penetration testing is a comprehensive security assessment method where testers have complete access to the internal architecture, design, and system details of the target. In this approach, the tester possesses full knowledge of the system’s infrastructure, including source code, network diagrams, and system configurations.
2. What is a white box penetration testing example?
An example of a white box test could involve analyzing the source code of a web application to identify vulnerabilities. Testers would scrutinize the code, look for potential security flaws, and examine the database structure and application logic to uncover weaknesses in the system.
3. What are black box grey box and white box penetration testing?
Black box, grey box, and white box penetration testing are distinct approaches used in security assessments to evaluate the vulnerabilities of a system. Here are the brief definitions of each type of penetration testing:
- Black box penetration testing: A security testing method where testers have no prior knowledge of the system. They approach it as an external hacker would, without any internal information about the system’s architecture or design.
- Grey box penetration testing: A security testing method where testers have partial knowledge of the system, such as limited access or some details about the internal architecture. This approach combines elements of both white and black box testing.
- White box penetration testing: A security testing method where testers have complete access to the internal architecture, design, and system details of the target. Testers possess full knowledge of the system’s infrastructure, including source code, network diagrams, and system configurations.
4. What is the difference between black box and white box penetration testing?
The main difference between black box vs white box penetration testing lies in the level of information and access the testers have. White box testing involves complete access to the internal structure, code, and system design. On the other hand, black box testing operates without any knowledge of the internal system; testers approach it as an external attacker.
5. What is more costly black box or white box penetration testing?
Typically, white box penetration testing is more resource-intensive and thus can be more costly. It demands a higher level of expertise, time, and resources due to the need for in-depth knowledge of the system’s internal workings, including analysis and evaluation of code, architecture, and configurations.
6. What is the white box penetration testing methodology?
White box penetration testing is not just a single test but a methodology involving a structured and systematic approach. It involves various steps such as reconnaissance, scanning, vulnerability assessment, exploitation, and reporting. The white box security testing methodologies focus on a deep dive into the internal workings of a system to identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities and security risks. White box testing is an essential part of a comprehensive security assessment, ensuring a thorough evaluation of system security from an insider’s perspective, and it plays a crucial role in strengthening the overall security posture of an organization’s infrastructure.
Final Thoughts About Whitebox Penetration Test
White box penetration testing serves as an effective method to strengthen software security. The level of complexity varies based on the application under assessment. Evaluating a small application that conducts straightforward operations is a swift process, often taking only a few minutes. However, larger applications necessitate significantly more time, ranging from days to weeks or even months.
Conducting these tests is crucial during the software development phase, both after its initial writing and following any subsequent modifications. Integrating white box penetration testing into your security strategy is pivotal, as it aids in preventing mistakes and oversights that could potentially expose your company to cyber threats.
If you are looking for experts in conducting white box testing for your IT environment or apps to check if they’re secure, don’t hesitate to contact LQA’s security testing team.









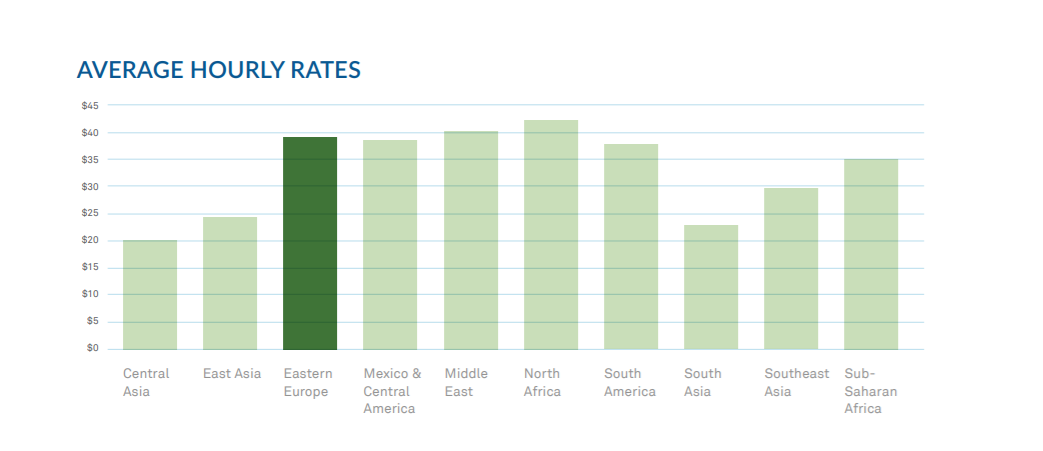
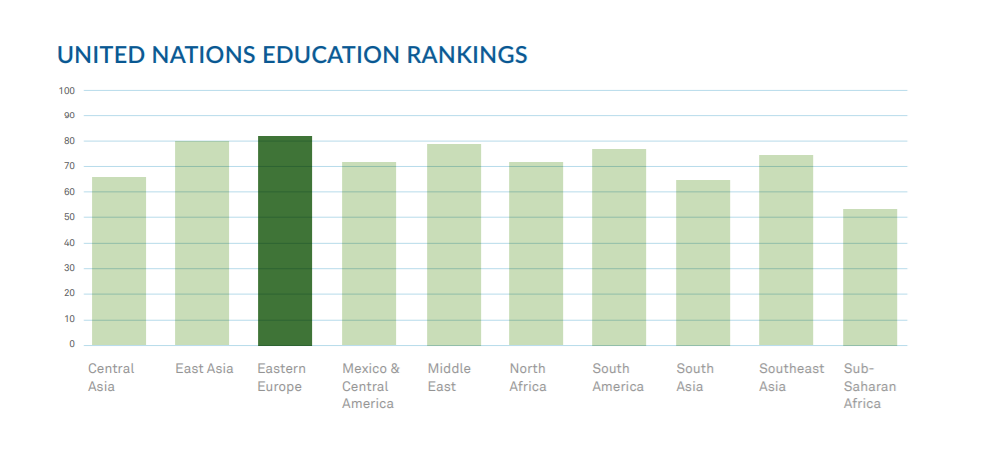
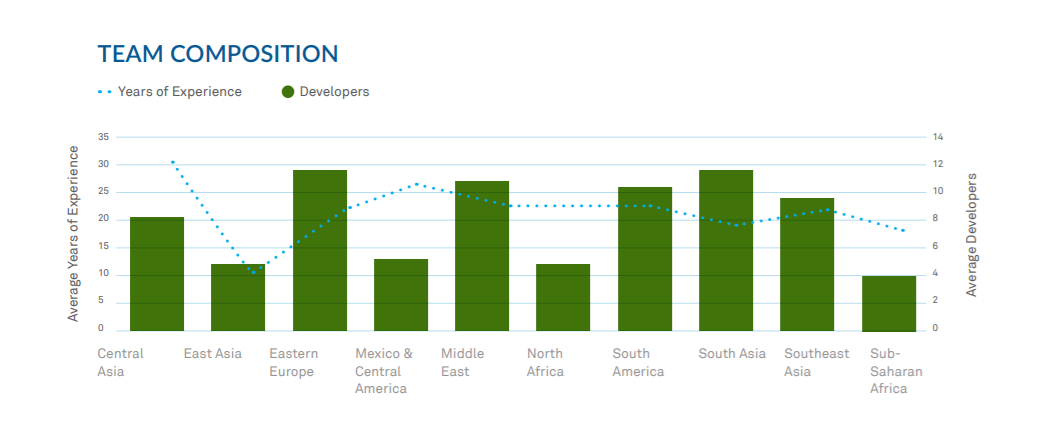 This is exacerbated by brain drain in many countries since many of the most experienced engineers may move on to other more promising regions. Eastern Europe suffered from a bit of brain drain in years past, but for the most part there are adequate opportunities available for software professionals and no need to leave to find work. The presence of so many seasoned professionals also feeds the IT ecosystem, which we’ll look into later in the report.
This is exacerbated by brain drain in many countries since many of the most experienced engineers may move on to other more promising regions. Eastern Europe suffered from a bit of brain drain in years past, but for the most part there are adequate opportunities available for software professionals and no need to leave to find work. The presence of so many seasoned professionals also feeds the IT ecosystem, which we’ll look into later in the report.