
In today’s digital age, cybersecurity testing is the cornerstone of a robust defense against cyber threats. In this article, we will delve into the world of cybersecurity testing, exploring the definition and significance of cybersecurity testing, the different types, why it’s crucial, the tools available, strategies for implementation, and how to measure success. Let our comprehensive guide help you strengthen your organization’s digital security.
What Is Cybersecurity Testing?
Before diving into the intricacies, let’s establish a foundational understanding of cybersecurity testing. At its core, cybersecurity testing refers to the process of evaluating an organization’s digital infrastructure, applications, and systems to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses that could be exploited by malicious actors.
Cybersecurity testing plays a pivotal role in the IT industry by serving as the first line of defense against cyber threats. It enables organizations to proactively identify vulnerabilities, assess risks, and implement robust security measures. This not only safeguards sensitive data but also helps maintain customer trust and compliance with regulatory requirements.

What Are the Different Types of Cybersecurity Testing?
Now, let’s delve into the heart of cybersecurity testing, exploring the various types of security testing and their specific purposes. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for tailoring an effective cybersecurity strategy.
Penetration Testing: What is Penetration Testing?
What is pen test? Cybersecurity penetration testing, or cybersecurity pen testing, simulates real-world cyberattacks to assess an organization’s security posture. Ethical hackers, known as penetration testers, attempt to exploit vulnerabilities to identify weaknesses in systems, networks, and applications.

Pros:
- Realistic Assessment: Provides a realistic view of an organization’s security preparedness.
- Identifies Critical Flaws: Uncovers vulnerabilities that could lead to severe breaches.
- Prioritizes Remediation: Helps prioritize vulnerabilities based on their criticality.
Cons:
- Resource-Intensive: Can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Limited Scope: Might not cover all potential attack vectors.
When to Use: Employ penetration testing when you need a comprehensive assessment of your organization’s security posture and want to identify critical vulnerabilities that could be exploited by cybercriminals.
Vulnerability Assessment
Vulnerability assessment focuses on identifying and prioritizing vulnerabilities within an organization’s IT infrastructure. This cybersecurity assessment test provides a comprehensive view of potential weaknesses, allowing organizations to allocate resources effectively to address critical issues first.

Pros:
- Systematic Evaluation: Offers a systematic approach to identifying vulnerabilities.
- Prioritization: Helps prioritize vulnerabilities based on potential impact.
- Regulatory Compliance: Assists in meeting compliance requirements.
Cons:
- Lacks Real-World Testing: Doesn’t simulate real attacks or exploitation.
- Possibility to Generate False Positives: Can sometimes flag non-exploitable issues.
When to Use: Utilize vulnerability assessments for regular, proactive monitoring of your organization’s security posture and prioritizing remediation efforts.
Security Auditing
Security auditing involves evaluating an organization’s security policies, controls, and practices to ensure they align with industry standards and best practices. It helps organizations identify gaps in compliance and security protocols.

Pros:
- Ensures Compliance: Helps ensure adherence to industry regulations and standards.
- Policy Alignment: Verifies that security policies align with best practices.
- Risk Mitigation: Identifies areas of risk in security controls.
Cons:
- Limited to Policies and Controls: May not assess vulnerabilities in systems.
- Doesn’t Simulate Attacks: Doesn’t simulate real-world attacks or exploits.
When to Use: Employ security auditing to validate compliance with industry standards and ensure security policies align with best practices.
Security Scanning
Security scanning uses automated tools to scan networks and systems for known vulnerabilities. This type of testing is essential for regular, proactive monitoring of an organization’s security posture.

Pros:
- Automation: Offers automated vulnerability detection.
- Regular Scanning: Enables continuous monitoring for threats.
- Quick Identification: Rapidly identifies known vulnerabilities.
Cons:
- Limited to Known Vulnerabilities: May miss zero-day vulnerabilities.
- Possibility to Generate False Positives: Automated scans can produce false alarms.
When to Use: Use security scanning for ongoing, automated vulnerability detection to quickly identify known vulnerabilities in your environment.
As applications move to the cloud and remote work increases, it’s easy to overlook misconfigurations. Gartner research predicts that 99% of cloud misconfigurations by 2025 will be the customer’s fault. To avoid this, companies need to pay close attention to network configurations and use security scans to enhance their cybersecurity.
Web Application Security Testing
Web application testing focuses on the security of web-based applications and websites. It assesses vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), web application penetration testing, and more to ensure the protection of sensitive user data.

Pros:
- Protects User Data: Ensures the security of user data in web applications.
- Prevents Attacks: Identifies and mitigates common web vulnerabilities.
- Enhances Trust: Builds trust with customers by safeguarding their information.
Cons:
- Resource-Intensive: Can be time-consuming for complex web applications.
- Requires Expertise: Requires testers with knowledge of web vulnerabilities.
When to Use: Employ web application testing when you need to secure web-based applications, especially those handling sensitive data or customer information.
Network Security Testing
Definition: Network security testing examines an organization’s network infrastructure for vulnerabilities and potential security threats. It includes assessments of firewalls, routers, switches, intrusion detection systems (IDS), network penetration testing, tests internet security, etc.
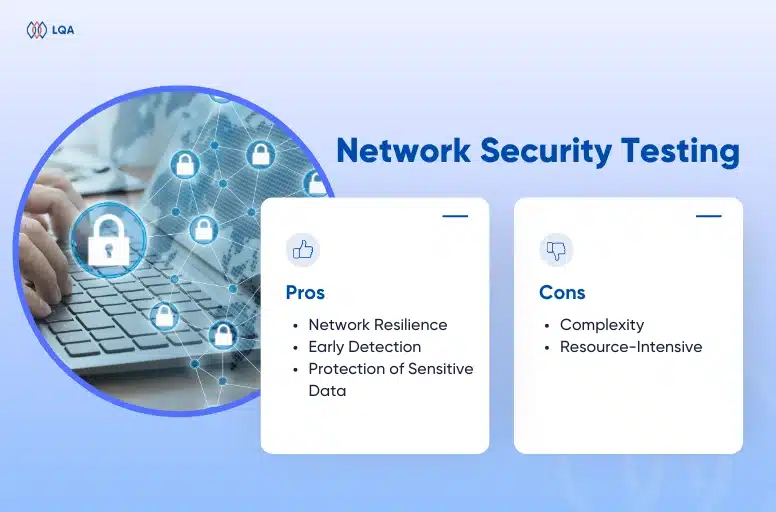
Pros:
- Network Resilience: Ensures the network infrastructure is resilient against cyber threats.
- Early Detection: Identifies weaknesses before they are exploited.
- Protection of Sensitive Data: Safeguards sensitive data in transit.
Cons:
- Complexity: Requires a deep understanding of network configurations and protocols.
- Resource-Intensive: This can be time-consuming for extensive networks.
When to Use: Implement network security testing when you need to assess the security of your network infrastructure, detect vulnerabilities, and ensure the protection of data in transit.
Mobile Application Testing
As mobile devices become ubiquitous, mobile application testing is crucial. It ensures that mobile apps are secure and that user data remains protected. This testing assesses vulnerabilities specific to mobile platforms.

Pros:
- Protects User Data: Safeguards sensitive user data stored and processed by mobile apps.
- Enhances App Trust: Builds trust with users by providing secure mobile experiences.
- Identifies Platform-Specific Issues: Addresses vulnerabilities unique to mobile platforms.
Cons:
- Diverse Platforms: Requires testing on multiple mobile operating systems.
- Evolving Threats: Needs constant updates to address emerging mobile threats.
When to Use: Employ mobile application testing when developing or deploying mobile apps to ensure user data security and protect against platform-specific vulnerabilities.
Cloud Security Testing
With the migration to cloud-based solutions, cloud security testing ensures the security of data stored and processed in the cloud. It covers configuration vulnerabilities, access control, and data encryption.

Pros:
- Cloud Data Protection: Ensures the security of data stored in cloud environments.
- Scalability: Scales with cloud adoption, accommodating growth.
- Compliance Assurance: Helps organizations meet regulatory requirements in the cloud.
Cons:
- Complex Cloud Ecosystems: Testing in diverse cloud environments can be complex.
- Shared Responsibility: Cloud security involves shared responsibility with the cloud provider.
When to Use: Utilize cloud security testing when migrating to or operating in cloud environments to protect data and ensure compliance in a shared responsibility model.
Data Security Testing
Data security testing assesses an organization’s measures to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, disclosure, or theft. It focuses on evaluating the security of data storage, transmission, and access controls.

Pros:
- Data Protection: Ensures the safeguarding of sensitive data, including customer information and proprietary data.
- Compliance Assurance: Helps organizations meet data protection regulations and industry standards.
- Prevents Data Breaches: Identifies vulnerabilities that could lead to data breaches.
Cons:
- Complexity: Requires a deep understanding of data encryption, access controls, and data handling processes.
- Resource-Intensive: Comprehensive data security testing can be resource-intensive.
When to Use: Implement data security testing when you need to evaluate the effectiveness of your data protection measures, ensure compliance with data privacy regulations, and prevent data breaches. This type of testing is crucial for organizations that handle sensitive customer or proprietary data.
Information Security Testing
Information security testing evaluates an organization’s overall information security posture. It assesses the effectiveness of security policies, controls, and procedures in protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access, breaches, and data leaks.

Pros:
- Comprehensive Security Assessment: Provides a holistic evaluation of an organization’s information security measures.
- Risk Mitigation: Identifies vulnerabilities and weaknesses that could lead to information security breaches.
- Regulatory Compliance: Assists in meeting compliance requirements related to information security standards.
Cons:
- Resource-Intensive: This may require substantial resources and time for thorough testing.
- Complexity: Evaluating the entire information security framework can be complex.
When to Use: Employ information security testing when you need a comprehensive assessment of your organization’s information security measures, want to identify vulnerabilities that could lead to data breaches or data leaks, and ensure compliance with information security standards and regulations. This type of testing is crucial for organizations that handle sensitive information, including personal data, financial records, and proprietary information.
The choice of cybersecurity testing type depends on the specific needs and risks faced by an organization. For instance, penetration testing is ideal for organizations seeking to identify critical vulnerabilities and understand the impact of potential cyberattacks, while Vulnerability assessments are beneficial for organizations looking to maintain an ongoing assessment of their security posture.
By tailoring the type of cybersecurity testing to their unique circumstances, organizations can better defend against potential threats.
Why Cyber Security Testing?
Every year, the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) conducts research on cybercrime. In 2020, incidents involving compromises to business email alone resulted in losses exceeding $1.8 billion. This figure doesn’t even encompass the various other ways in which cyber threats can affect businesses. Given the multitude of security vulnerabilities, cybersecurity assessments hold significant value for businesses of all scales.
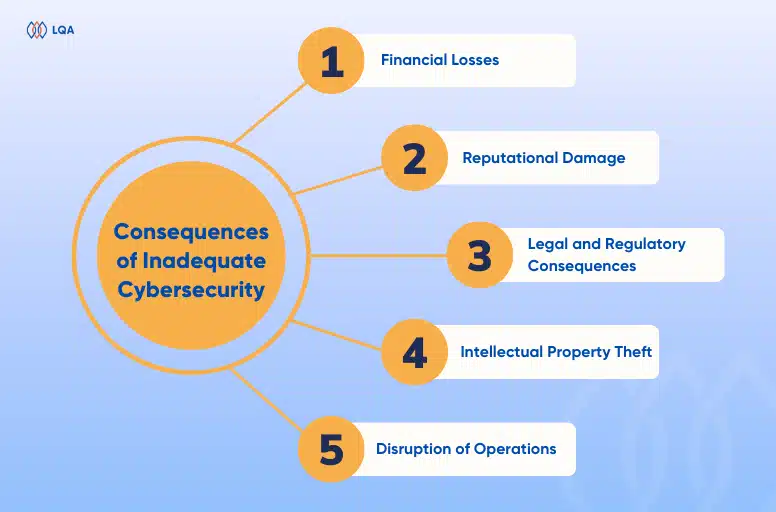
The consequences of inadequate cybersecurity testing can be severe, ranging from financial losses to severe damage to an organization’s reputation:
- Financial Losses: Cyberattacks can result in substantial financial losses. These losses can stem from theft of sensitive data, the cost of remediation, legal fees, and regulatory fines. In some cases, the financial impact can be devastating, leading to business closures.
- Reputational Damage: A cybersecurity breach can tarnish an organization’s reputation, eroding customer trust and confidence. Once trust is lost, it can be challenging to rebuild, potentially leading to customer churn and loss of market share.
- Legal and Regulatory Consequences: Non-compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR or HIPAA, can result in hefty fines. Inadequate cybersecurity measures can lead to legal actions, further exacerbating financial losses.
- Intellectual Property Theft: For technology companies, intellectual property theft is a grave concern. Cybercriminals can steal valuable IPs, compromising an organization’s competitive advantage.
- Disruption of Operations: Cyberattacks can disrupt business operations, leading to downtime, loss of productivity, and additional costs associated with recovery.
The financial and reputational risks associated with security breaches underscore the critical importance of cybersecurity testing. Organizations that prioritize cybersecurity testing are better equipped to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by cybercriminals.
Choosing the Right Cyber Security Testing Tools
Selecting the appropriate cybersecurity testing tools is a crucial aspect of building a robust security framework. Here, we introduce a variety of cybersecurity testing tools and provide criteria for making informed choices that align with your organization’s specific requirements.
A Variety of Cybersecurity Testing Tools
The market offers a diverse range of tools to cater to different testing needs, including:
- Wireshark: Wireshark is a widely used network protocol analyzer. It helps security professionals examine network traffic, detect anomalies, and identify potential security threats.
- Burp Suite: Burp Suite is a comprehensive web vulnerability scanner and proxy tool. It aids in web application testing by identifying vulnerabilities like SQL injection and cross-site scripting.
- OpenVAS: OpenVAS is an open-source vulnerability scanner designed for detecting vulnerabilities in networks and web applications. It provides regular updates for the latest threats.
- Nessus: Nessus is a widely trusted vulnerability assessment tool that scans networks, systems, and applications for vulnerabilities. It offers a vast database of known vulnerabilities.
- Snort: Snort is an open-source intrusion detection and prevention system (IDPS). It monitors network traffic for suspicious activity and can block threats in real-time.
- OWASP ZAP: The OWASP Zed Attack Proxy (ZAP) is a popular open-source web application security scanner. It helps find vulnerabilities in web applications during development and testing.
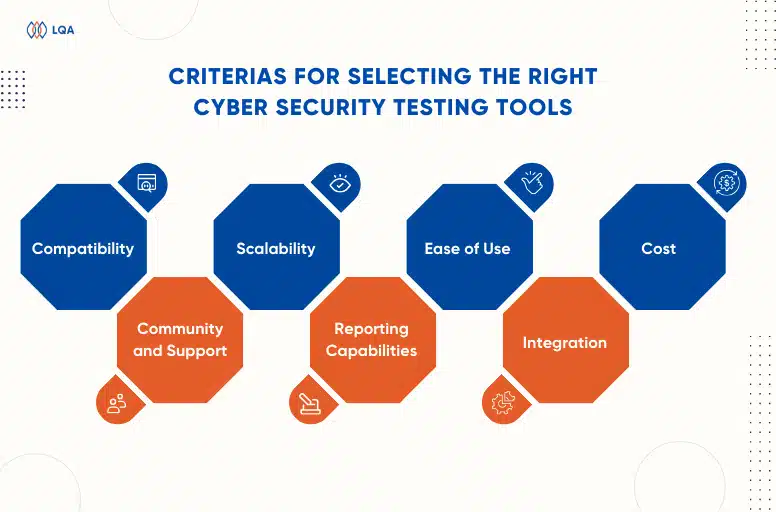
Criteria for Selecting Suitable Tools
When choosing cybersecurity testing tools, consider the following criteria to ensure they align with your organization’s specific needs:
- Compatibility: Ensure that the tool is compatible with your organization’s infrastructure, systems, and platforms.
- Scalability: Choose tools that can scale with your organization’s growth and evolving security requirements.
- Ease of Use: Opt for tools with user-friendly interfaces and adequate documentation to expedite the testing process.
- Reporting Capabilities: The tool should generate comprehensive reports that are easy to understand, enabling efficient remediation of vulnerabilities.
- Community and Support: Assess the tool’s community and support resources. Active communities and professional support can be invaluable when troubleshooting issues.
- Cost: Consider the tool’s pricing structure, including licensing fees, subscription costs, and ongoing maintenance expenses.
- Integration: Ensure that the tool can integrate seamlessly with your existing cybersecurity infrastructure and other security tools.
By carefully evaluating these criteria, you can select the most suitable cybersecurity testing tools to bolster your organization’s security defenses.
How To Implement an Effective Cyber Security Test Strategy
Establishing an effective cybersecurity testing strategy is paramount to safeguarding your organization’s digital assets. Here, we provide a step-by-step guide to help you create a robust testing strategy that aligns with your specific organizational needs.
10 steps to implement effective cybersecurity testing strategy
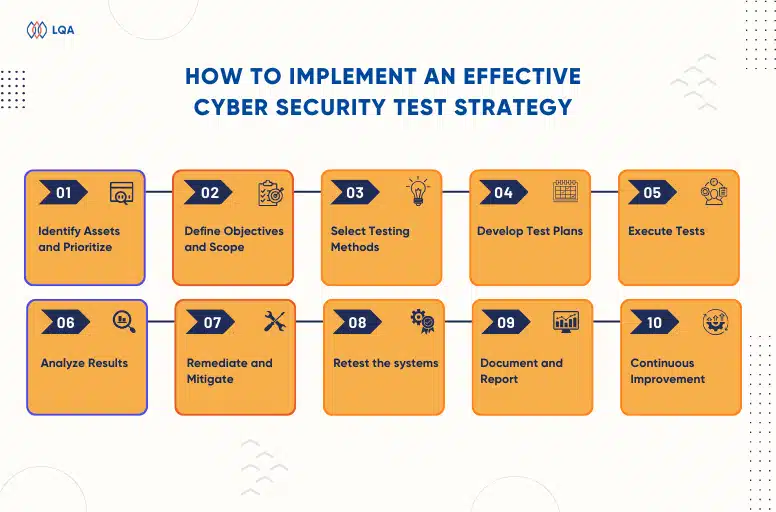
Step 1: Identify Assets and Prioritize
Begin by identifying the critical assets within your organization, including data, applications, and systems. Prioritize these assets based on their importance and potential impact on the organization in case of a security breach.
Step 2: Define Objectives and Scope
Clearly define the objectives of your cybersecurity testing efforts. Determine the scope of testing, specifying which systems, networks, and applications will be assessed, as well as the types of tests to be conducted.
Step 3: Select Testing Methods
Choose the appropriate cyber security methodologies, such as penetration testing, vulnerability assessments, or web application testing, based on your identified objectives and scope. Ensure that these methods align with your organization’s unique security challenges.
Step 4: Develop Test Plans
Create detailed test plans that outline the specific tests to be conducted, including the tools and techniques to be used. Test plans should also include a timeline and responsibilities for the testing team.
Step 5: Execute Tests
Execute the tests according to the defined plans. During this phase, ethical hackers or cybersecurity experts simulate attacks and attempt to uncover vulnerabilities and weaknesses.
Step 6: Analyze Results
Thoroughly analyze the results of the tests, identifying vulnerabilities and assessing their severity. Prioritize vulnerabilities based on the potential impact and exploitability.
Step 7: Remediate and Mitigate
Develop a remediation plan to address identified vulnerabilities promptly. Ensure that your organization’s IT team or external experts can implement fixes and improvements.
Step 8: Retest the systems
After remediation, retest the systems to verify that vulnerabilities have been effectively addressed. This step validates the effectiveness of your security measures.
Step 9: Document and Report
Maintain detailed records of all testing activities, findings, and remediation efforts. Create comprehensive reports for stakeholders and regulatory compliance purposes.
Step 10: Continuous Improvement
Cybersecurity testing is an ongoing process. Continuously assess and refine your cybersecurity testing strategy to adapt to evolving threats and technologies.
Remember that a one-size-fits-all approach to cybersecurity testing may not be effective. Customize your testing strategy to address your organization’s unique risks and challenges. Furthermore, integrate testing seamlessly into your development lifecycle to identify and rectify vulnerabilities early in the process.
How To Measure and Monitor Cybersecurity Testing Success
Measuring and monitoring the success of your cybersecurity testing efforts is crucial to ensure that your organization remains secure. Here, we provide guidance on setting measurable goals and tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) to gauge the effectiveness of your testing strategy.
Setting Measurable Goals
Setting clear and measurable goals is a fundamental aspect of an effective cybersecurity testing strategy. Let’s define objectives that align with your organization’s security needs and priorities.
- Vulnerability Reduction: Set a goal to reduce the number of vulnerabilities over time. Monitor the percentage decrease in vulnerabilities after each testing cycle.
- Incident Response Time: Measure the time it takes to detect and respond to security incidents. Aim for a reduction in incident response time to minimize potential damage.
- Patch Management: Track the time it takes to apply security patches and updates after vulnerabilities are identified. Strive for faster patch management to reduce exposure.
- Compliance Metrics: Ensure that your organization complies with relevant regulations and standards. Measure your level of compliance and work towards 100% adherence.
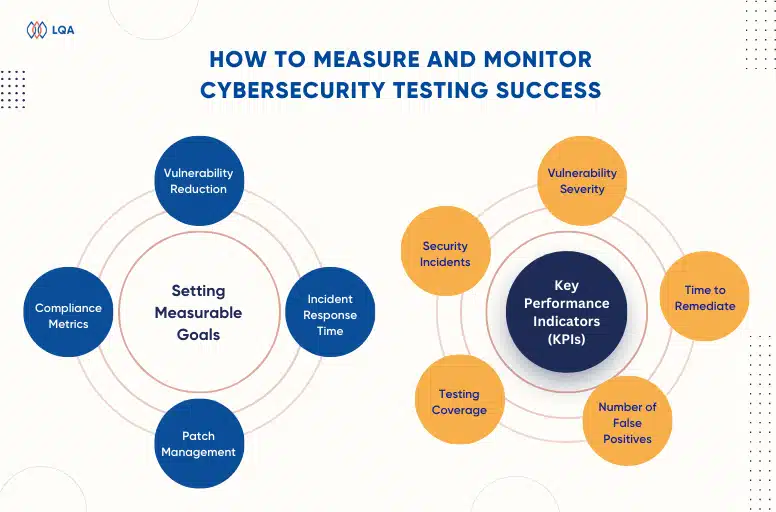
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are essential for tracking and measuring the success of your cybersecurity testing program. Let’s explore the crucial KPIs that help gauge the effectiveness of your testing efforts and provide insights for continuous improvement:
- Vulnerability Severity: Monitor the severity levels of vulnerabilities detected. Focus on reducing the number of high-severity vulnerabilities.
- Time to Remediate: Measure the average time it takes to remediate identified vulnerabilities. A shorter time indicates efficient vulnerability management.
- Number of False Positives: Keep track of false positives generated during testing. Minimizing false positives helps focus resources on genuine security threats.
- Security Incidents: Track the number of security incidents over time. Aim to reduce incidents, demonstrating improved security posture.
- Testing Coverage: Assess the percentage of systems, networks, and applications covered by cybersecurity testing. Strive for comprehensive coverage.
By setting clear goals and monitoring these KPIs, you can assess the effectiveness of your cybersecurity testing program and make data-driven improvements.
Lotus Quality Assurance’s Cybersecurity Testing Services
Lotus Quality Assurance (LQA) stands as one of the pioneering independent Software Testing Companies in Vietnam. We’ve expanded our reach with subsidiaries in Japan and the United States, enabling us to seamlessly cater to clients’ quality assurance needs across diverse domains, transcending geographical boundaries.
Over the years, LQA has honed industry-specific expertise to support our clients’ growth effectively. Our passionate and talented team’s unwavering commitment has garnered trust from clients in the most demanding markets, including the USA, Japan, Korea, and more.
We understand the challenges that you, as decision-makers have to face, in how to balance between quality and cost-efficiency. We aim to deliver a customized software QA solution package for your business’s requirements. We stand out by:
Industry Specialization
LQA’s industry specialization ensures that we not only meet your requirements but also exceed your clients’ expectations efficiently.
As Vietnam’s first independent software testing company, we boast over seven years of experience in safeguarding and detecting all software bugs and issues before market delivery.
Our QA solutions and processes have earned recognition through international and prestigious awards and certifications in software testing, including ISTQB (International Software Testing Qualifications Board), PMP (Project Management Professional), and ISO.

Compliance with TCoE
LQA’s commitment to Testing Center of Excellence (TCoE) compliance empowers us to provide your testing projects with a seamless blend of top-notch resources and methodologies, ensuring exceptional results and client satisfaction.
Advanced Technology
Leveraging cutting-edge testing devices, tools, and frameworks, our team guarantees the smooth operation of your software, delivering a flawless user experience and a competitive market advantage. With our advanced technological solutions, you can confidently detect all potential bugs and issues promptly before they impact your users.

Professional Certificate of 150 QA Engineers
Our 150 highly-skilled software testing engineers hold prestigious international certifications such as ISTQB, PMI, PSM, and more. Continuous learning and skill refinement are integral to our engineers’ daily routine, ensuring they stay at the forefront of industry best practices.

Proven Track Record
When it comes to reliability, our track record speaks volumes. Esteemed organizations, including TOSHIBA, Panasonic, SK Telecom, LG Electronics, MB Bank, Infiniq, SQC, Perxtech, Verb Data, Ascentis, Qualcomm, Kick ID, and many more, have entrusted their faith in our solutions. Our software testing case studies can help you delve deeper into our expertise and experience.

Choosing Lotus Quality Assurance means partnering with a proven leader in software testing, backed by a passionate team, industry specialization, cutting-edge technology, and a commitment to excellence.
Frequently Asked Questions About Cyber Security Testing
1. What is cybersecurity testing?
Cybersecurity testing is the process of evaluating an organization’s digital infrastructure, applications, and systems to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses that could be exploited by malicious actors. It involves various types of tests, such as penetration testing, vulnerability assessment, and web application testing, to assess and enhance an organization’s security posture.
2. When should we conduct cybersecurity testing?
Cybersecurity testing should be conducted regularly and as part of an ongoing security strategy. It should occur whenever there are significant changes in your IT infrastructure, applications, or systems. Additionally, routine testing, such as vulnerability assessments, should be performed on a scheduled basis to proactively identify and address vulnerabilities.
3. What qualifications should we look for in a cybersecurity testing vendor?
When selecting a cybersecurity testing vendor, consider their experience, expertise, and certifications in the field. Look for certifications such as Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), and Certified Information Security Manager (CISM). Additionally, check references and review their track record of successful testing engagements.
4. What are the 5 stages of penetration testing?
Before digging deeper into the comprehensive penetration testing process, let’s find out what is penetration testing in cyber security.
Penetration testing definition: Penetration testing is a cybersecurity practice where ethical hackers simulate cyberattacks to find vulnerabilities in systems, helping organizations improve their security.
Here are the five crucial stages of penetration testing:
– Planning: Define the scope, objectives, and rules of engagement for the penetration test.
– Information Gathering: Gather information about the target system, including IP addresses, network topology, and potential vulnerabilities.
– Vulnerability Analysis: Identify and assess vulnerabilities in the target system, including configuration weaknesses and software vulnerabilities.
– Exploitation: Attempt to exploit identified vulnerabilities to gain access to the system, mimicking real-world cyberattacks.
– Reporting: Document the findings, including vulnerabilities discovered, their severity, and recommendations for remediation. Provide a comprehensive report to the client or organization.
These stages are essential for conducting thorough and effective penetration testing.
Final Thoughts About Cyber Security Testing
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, cybersecurity testing is not an option but a necessity for organizations in the IT industry. The consequences of inadequate testing can be devastating, leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory non-compliance. By understanding the various types of cybersecurity testing, choosing the right tools, implementing effective testing strategies, and measuring success, organizations can fortify their defenses against cyber threats.
Furthermore, staying ahead in the cybersecurity landscape requires organizations to embrace emerging trends and continuously adapt their testing approaches. As cybersecurity threats evolve, so must our defenses.
Remember, cybersecurity is a complex and ever-evolving field. It demands a proactive approach and a commitment to ongoing improvement. Whether you choose to build an in-house testing team or partner with a specialized vendor like Lotus Quality Assurance or any other top software testing companies in the world, the key is to prioritize cybersecurity testing as an integral part of your IT strategy.
Through LQA’s cybersecurity consultations and solutions, we have the ability to implement tailored solutions for your business. Whether you need us to augment your existing IT team or provide comprehensive support, we’re here to assist. Reach out to one of our experts today to explore our capabilities further. We eagerly anticipate the opportunity to collaborate with you!






